reactive power
The dissipated power resulting from inductive and capacitive loads measured in and symbolized by the letter Q.
In electrical grid systems, the power that flows back from a destination toward the grid in an alternating current scenario. In a direct current system, the voltage and load is static, and the direction of energy is "one way," but in alternating current, there are different phases.
For sinusoidal quantities in a two-wire circuit, reactive power is the product of the voltage, the current, and the sine of the phase angle between them with the current taken as reverence. In a polyphase circuit, it is the sum of the reactive powers of the individual phases.
The following figure is the Power Triangle. The Power Triangle relates true (P), reactive (Q), and apparent power (S) in trigonometric form.
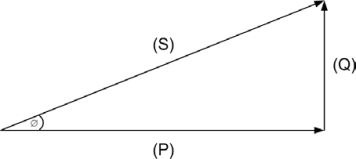
Reactive power is also known as phantom power or wattless power. See also kVAR lead.